Embryology
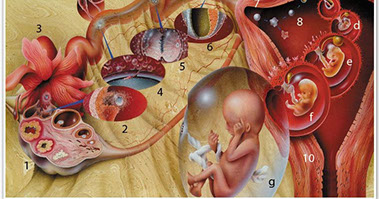
Embryology
Embryology is the branch of biology that studies the prenatal development of gametes (sex cells), fertilization, and development of embryos and fetuses.
What is human embryology?
Human embryology is the study of this development during the first eight weeks after fertilisation. The normal period of gestation (pregnancy) is nine months or 38 weeks. The germinal stage refers to the time from fertilization through the development of the early embryo until implantation is completed in the uterus.
What are the stages of embryonic development?
The germinal stage is the period of gestation from fertilization or conception, when the egg meets the sperm, to implantation of the embryo in the uterus. The embryonic stage of gestation is the period after implantation, during which all of the major organs and structures within the growing mammal are formed.
Who is an embryologist?
Career Definition: Embryologist. Embryologists most commonly work with physicians to assist their patients with reproductive health issues and clinical research. Clinical embryologists are responsible for retrieving eggs, assisting with in vitro fertilization, maintaining clinical records and running tests on eggs.
EMBRYO FREEZING AND VITRIFICATION
Usually after a cycle of IVF / ICSI treatment, there are some successfully fertilised embryos that we have not transferred to the patient. These surplus embryos can be frozen and stored for future use
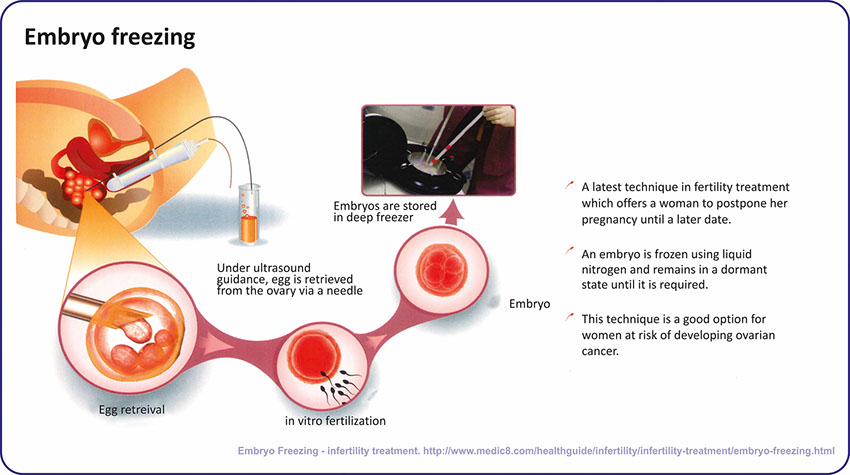
Cryo-Preservation (Freezing)
In a single IVF cycle, a large number of embryos are sometimes produced. When transferring embryos back into the uterus we try to avoid twin/triplet pregnancy, and therefore more than 3 embryos are rarely transferred. Thus, at the end of a treatment cycle, extra embryos may be frozen and used in the future in case the patient does not conceive or if she returns for treatment again after completing her pregnancy.
Freezing is done with the aid of an embryo freezer and the embryos are frozen in straws and transferred into liquid nitrogen dewars.

